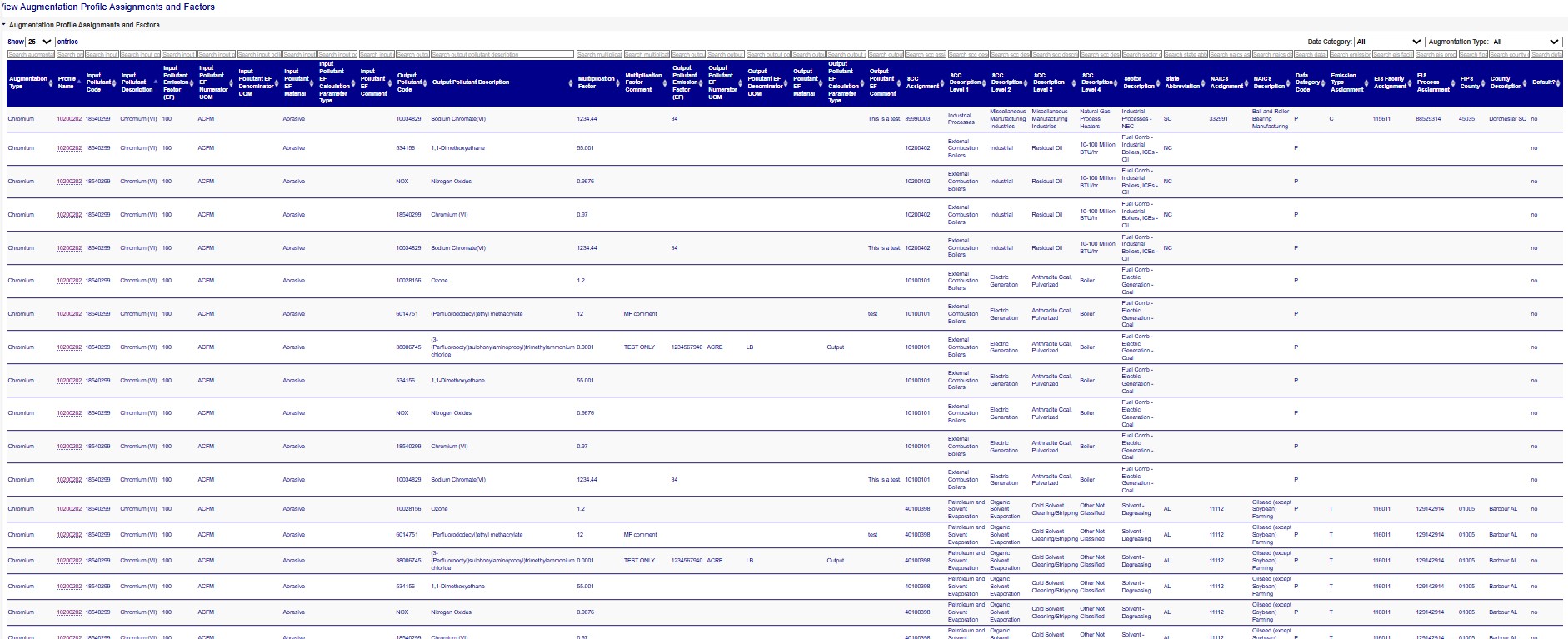
Augmentation Multiplication Factors and Assignments
This data table view displays a composite table that provides a comprehensive view of all the combinations of output pollutants and assignment information associated with a given profile.
Within the table, you have the option to filter by Augmentation Type from the drop down menu above the table; filter each column by typing text into the search box above each column and; sort the column results by ascending or descending alpha or numeric order. You may also download your data table results in a CSV file by clicking the CSV link below the table.
Augmentation Profile Factors
The profile name column displays clickable links that navigate to the Augmentation Profile Details page. Clicking on the link will display additional details for the Augmentation Profile in a single view including the Augmentation Profile Factors and the Assignments.
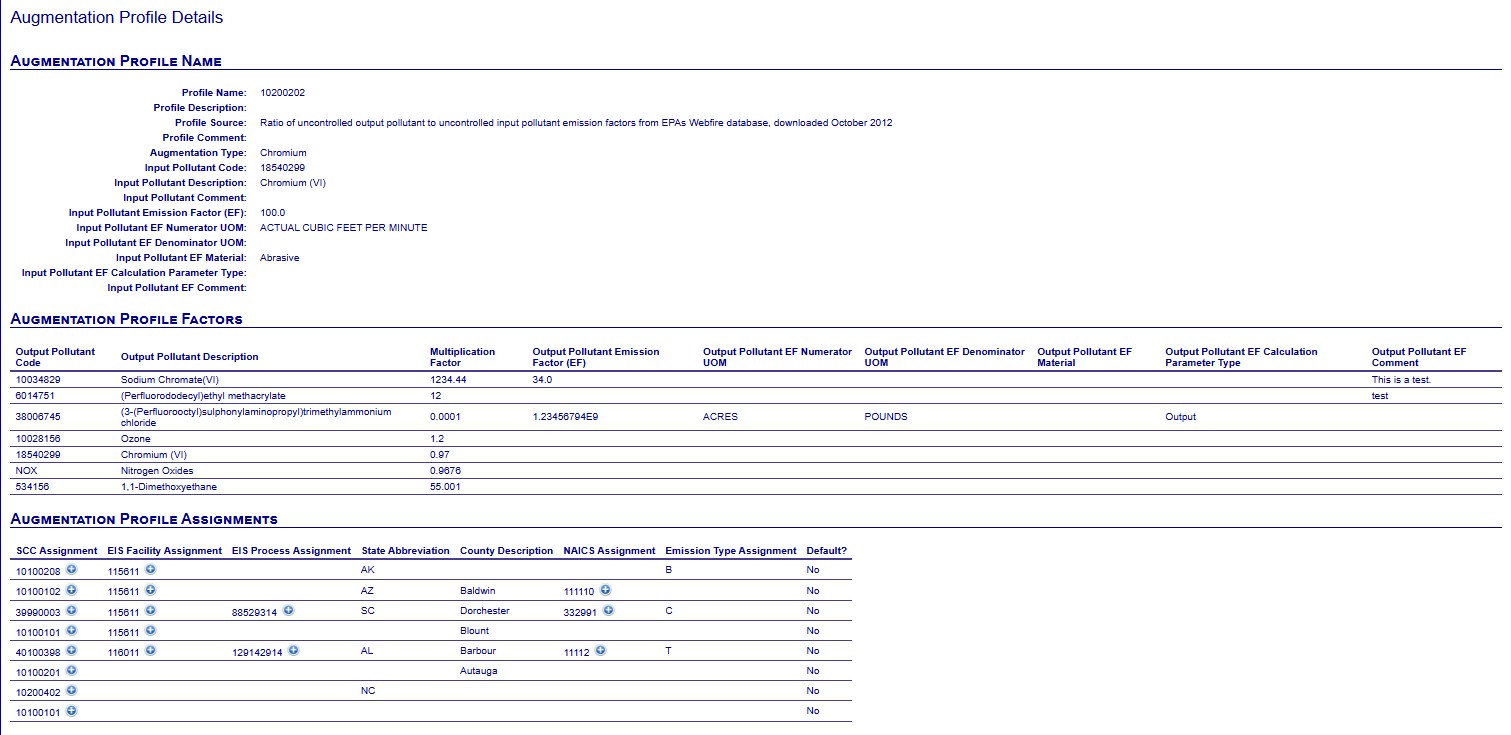
Augmentation Profile Details
Components
Profiles
A profile provides a description of the process for which a set of augmentation multiplication factors are created. This description is unique. In addition to the description, the source of how the factors are formed is displayed. A profile will belong to a type of augmentation (such as “Chromium Augmentation” or “HAP Augmentation”). Each profile should have a description and an augmentation type defined.
Example: “combust wood - wood bark waste- 20 percent moisture”
Profile Input Pollutants
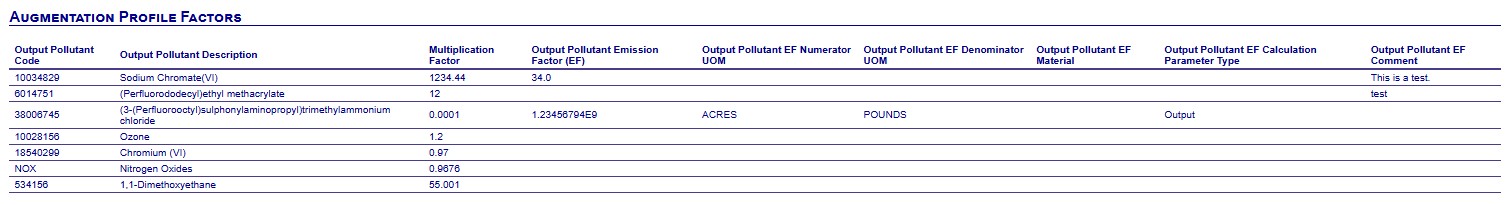
Each profile will have at least one input pollutant but may have more than one. The input pollutant determines the value that will be used to augment the data. For example, if this were a “Chromium” type of speciation factor, the input pollutant would be “Total Chromium”. If this were a “HAP” type of speciation factor, then the input pollutants for a profile may be “VOC”, “SO2”, and/or some form of particulate matter. The combination of the Profile and Input Pollutant will be unique.

Profile Output Pollutants
For each profile – input pollutant combination, a set of output pollutants (along with the multiplication factor to apply) is defined. To use the “Chromium” augmentation example, there would be two output pollutants: “Trivalent Chromium” and “Hexavalent Chromium”. For each output pollutant, a multiplication factor will be provided.
Augmentation Profile Factors
Profile Assignments
For each profile – input pollutant combination, information on what records can be applied is defined by its Profile Assignment attributes. A profile assignment can be assigned based on the following components shown in priority order:
- EIS Emissions Process ID (Point Only)
- EIS Facility Site ID (Point Only)
- County
- State
- Emissions type Code (Non-Point, On-Road, and Non-Road only)
- Source Classification Code (SCC)
- Regulatory Code
- NAICS Code (Point Only)
- Default if none of the other characteristics apply (used for chromium augmentation only)
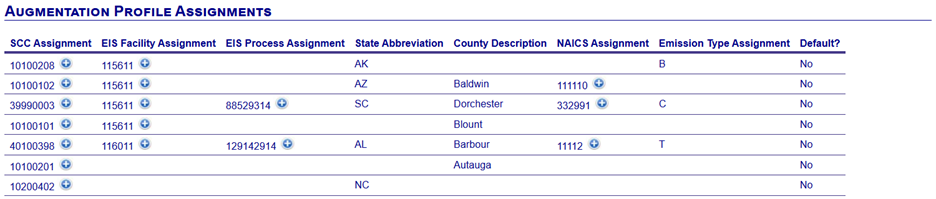
A profile assignment may be defined by one or more components. There is also a “default value” if there isn’t a profile assignment specifically defined. A given emissions record may meet the definitions of multiple profile assignments. In this case, the “most restrictive” record should be used. For example, if a profile assignment for SCC “12345678” exists and a profile for SCC “12345678” in the state of “NC” exists, if the record under consideration is in NC and has an SCC of “12345678”, the profile for “12345678” and “NC” would be used.
The combination of the EIS Process ID, EIS Facility ID, SCC, Emissions Type, Regulatory Code, NAICS Code, State Code, and Default indicator must be unique for a given Augmentation Type (not by Profile – Pollutant combination).
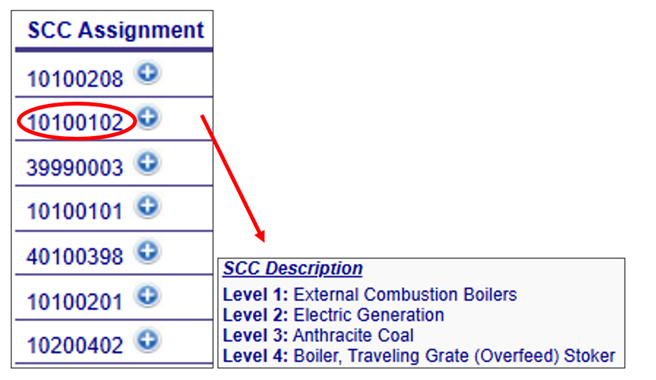
SCC Assignment
EIS Facility Assignment
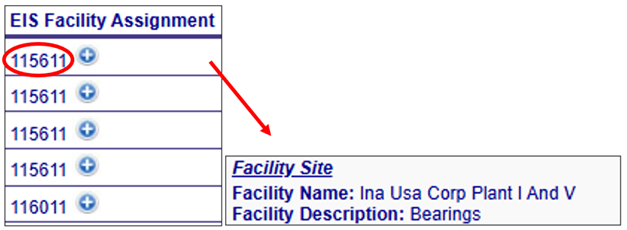
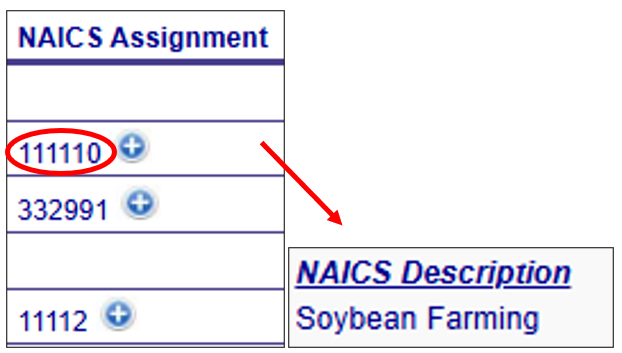
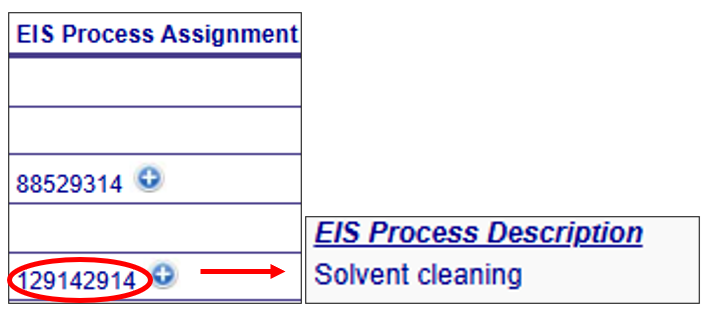
Additional information about the Augmentation Profile Assignment components can be viewed by clicking on the “plus” icon next to the assignment in the Augmentation Profile Assignments table. A pop out box will provide a more detailed description of the specific profile assignment component as shown below.
EIS Process Assignment
NAICS Assignment